Guide to Multilingual sites with Drupal 8

We are currently living in a globalized world. Thanks to the internet, the days when companies and businesses had to think in only one specific community as their marketing target have been left behind. Now, through your website, you may reach clients everywhere in the world with no further effort. But this comes with new challenges, language being the main one. Even if English usage has increased significantly, not all your potential clients speak or read it; or even if they do, they usually will prefer to get the information in their native language.
For this reason, if you want to extend your business to these markets, the first thing to do is to create a multilingual site. And that is what we will do using Drupal8. Thanks to its architecture, you may not only translate your current website and its content but you may also create specific content for a targeted language. That way, your business may connect in a better way with different communities and get more clients in the process. So, Let’s start!
1. Installation
For this blog purpose, we will start with a fresh Drupal 8 installation. There is no special consideration here; so you may install Drupal normally.
2. Installing language modules
By default, Drupal8 is not configured to support multilingual content. For this reason, the first thing to do after installing it is to activate the language modules. For this, go to /admin/modules and activate these four modules:
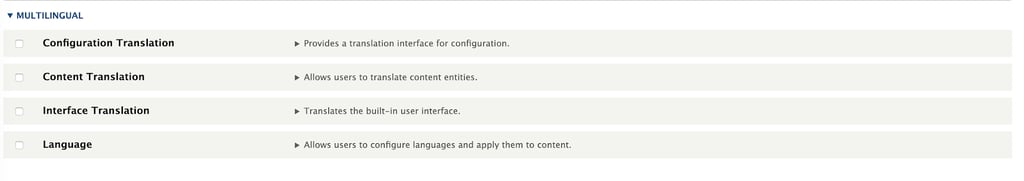
Once you have activated them, you will receive two warning messages along with the confirmation that the modules were successfully activated:

The first warning message is related to adding the languages our site will support and the second one is related to content configuration. We will check these in the next items.
3. Adding languages to our site
Once we have activated the language modules, we need to add some languages to our site. For this, go to admin/config/regional/language. There, you will see a screen similar to this:
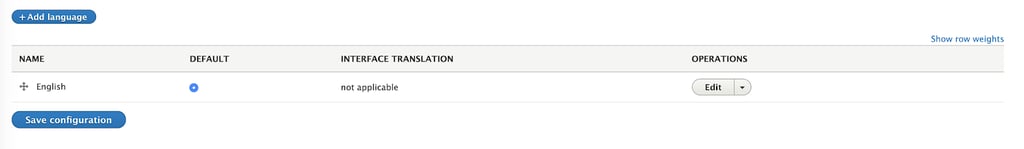
Click in add language and search for the language you want to support. For this example, we will support English and Spanish. Once you have selected the language, a progress bar will appear while Drupal installs the available translations and updates the configuration. After it has finished, it will return you to the first language screen, but the new language will appear listed:
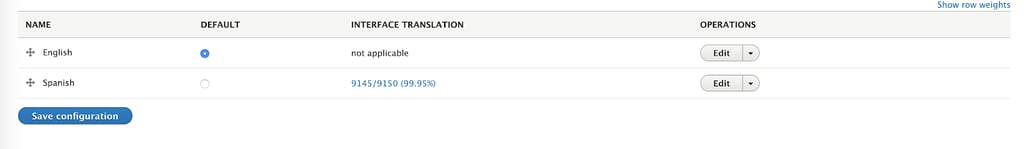
As you may see, you may select the newly added language as your default one. As well, it tells us how much of the drupal interface is translated to the new language. This is because Drupal allows you to use the admin interface in the language, or languages, your site is supporting for convenience. This is especially useful if, for example, the content in the new language is going to be managed by one of your company’s abroad offices.
4. Configuring content translation
The next step is to configure our content. One of the main advantages of Drupal 8 is that it allows us to control what we want to translate and what should always stay in the original language. To configure our content, go to admin/config/regional/content-language. There, you will find a similar page, like this:
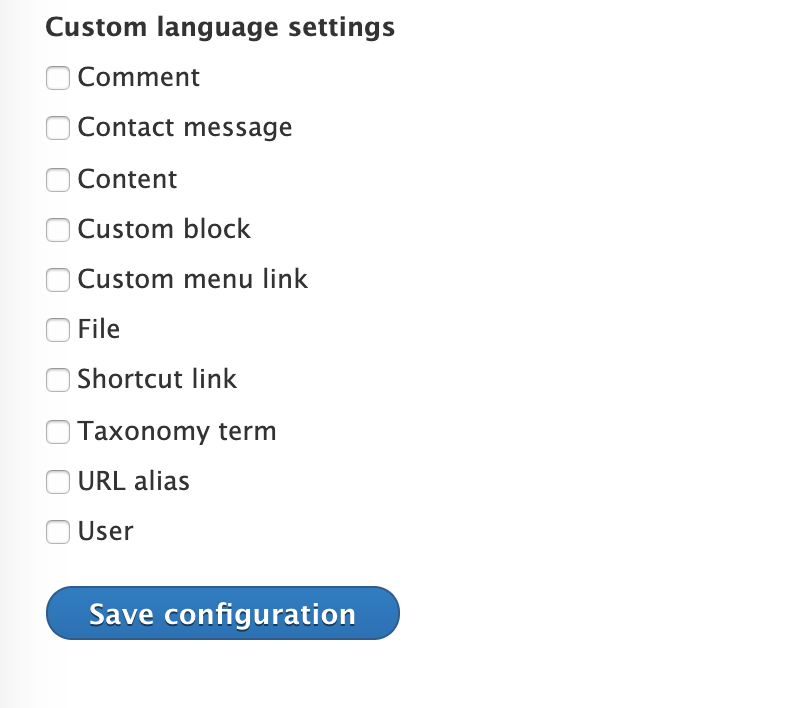
As you may see, we are able to translate everything in our Drupal site. For this example, we will only translate content. For this reason, select it. A new section of the page will appear
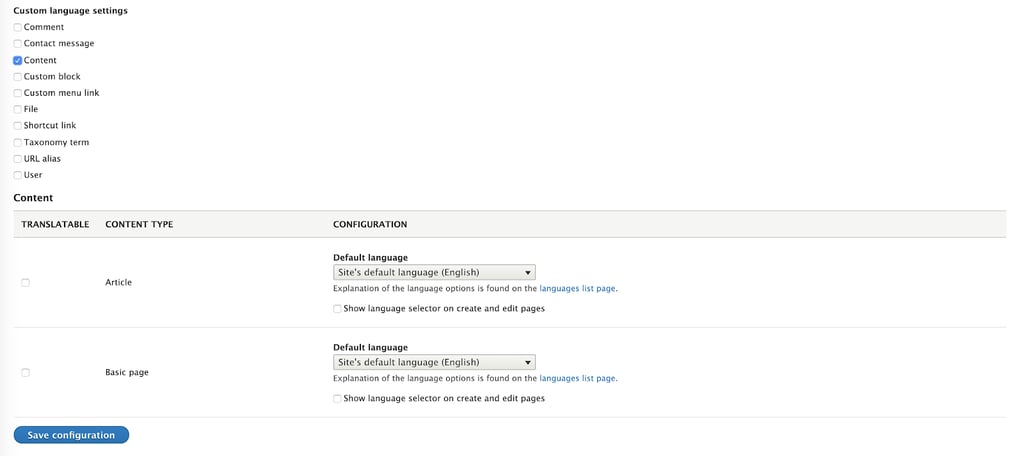
This lets us decide what content will be translated, and what fields of that content we will translate. After selecting a content type, a new section will appear with the fields we want to make translatable. For now, we will leave it as default, with all fields selected

After selecting the content types you want to translate, and configuring their fields, do not forget to click save.
5. Adding language switch block
So, now your content may be translatable. But, how would your visitors change from one language to another? Well, when we activated the language modules, Drupal automatically added a language switch block. We will add it to our site. Considering it is a regular block, go to admin/structure/block and add the block where you would want to display it. For this example, we will use the “sidebar second” region to display this block, called “Language switcher”.
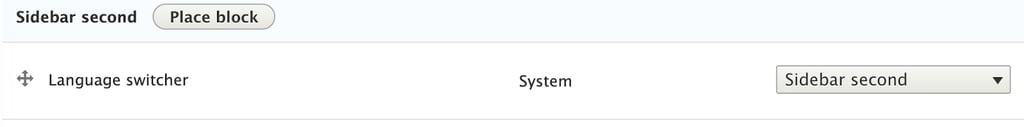
Once we save our blocks configuration, it will appear on our website.

As you may see, it allows the visitors to switch between the supported languages.
6. Translating your content
The last step is to start translating your content. For our example, we will create a hello world page. For now, it has no further considerations.

Once it is created, you may see that a “translate” tab has appeared in the admin interface. We will click there
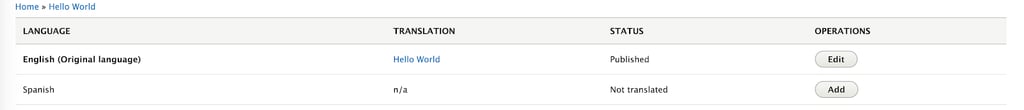
A new menu will appear with all available translations for our content. As you may see, considering that we have not translated the page yet, there will only be the original language page. Now, we will click on add item in the Spanish row.
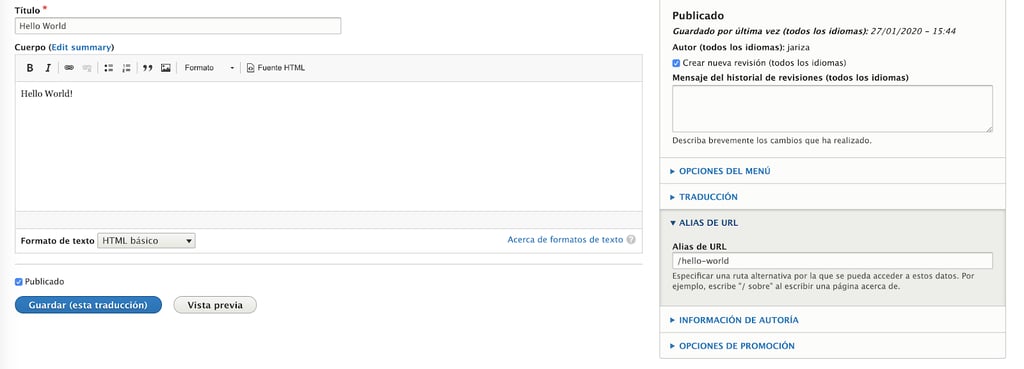
It will open an editor with the original content, but its interface will be in the selected language. There, we may translate the page. Once we have translated the content, hit on save this translation (or, for this case, on “guardar esta traducción”)
And that’s it! Our new page has been translated

Now, when visitors select the Español item in the language switch, they will see the page in Spanish!
And that’s it! With these six steps you may start creating content in different languages on your Drupal website. If you want to keep exploring multilingual features, you may check chapter 10 in the official Drupal 8 user guide.
Being able to display information in different languages is crucial for most businesses nowadays. These allow you not only to reach different countries around the globe but also to connect to those communities that may not use your native language and to break the communication barriers between your company and them. I hope that this guide will be the first step in a positive and outbreaking growth of your business!


